关于 C#事件解析
一. 什么是事件
1. 字面说明
事件(Event): 通俗的解释就是“能够发生的事情”,并且事件都是隶属于某一个主体的,比如公司上市,那个上市这个事件就是隶属于公司。
由上面的定义就可以知道,将事件抽象到代码当中就是,事件要隶属于一个类,也就是一个类的成员。
在前面就已经讲过:
- 属性:让对象有了访问数据的功能
- 方法:让对象有了对数据加工的功能
- 事件:让对象有了通知能力,使对象有了能通风报信的成员
2. 举个例子
- 手机:具备时间的对象
- 人:接受事件的对象,思考的过程就是事件处理器
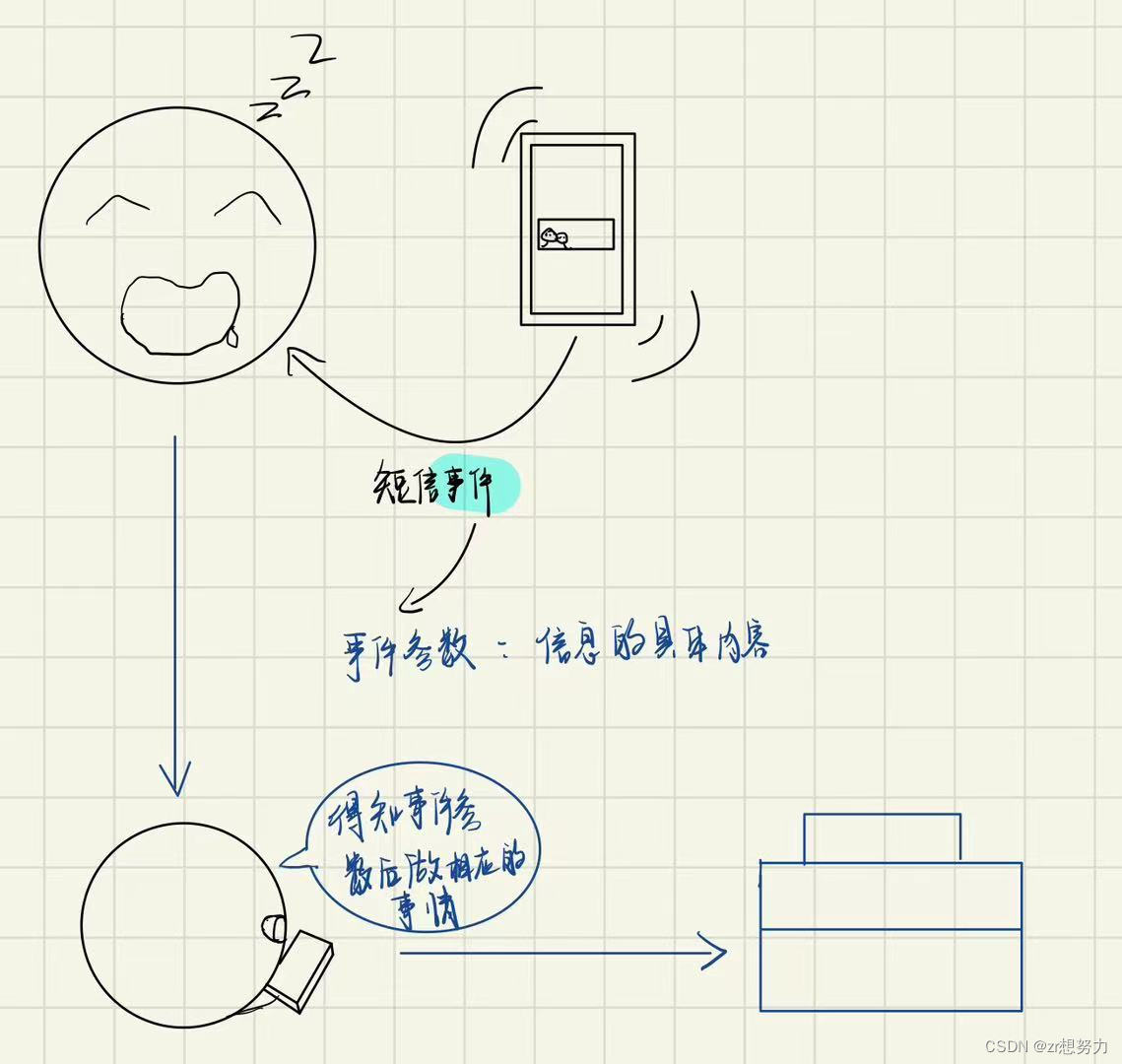
总的来说
根据事件参数来响应事件。
原理
事件模型的两个“5”:
- “发生->响应”的五个部分:
- “孩子 饿了 我 做饭”
- “闹钟 响了 我 上班”
其中的第五个部分存在订阅关系:“这个孩子是由我来响应的”,“这个闹钟是我的”。也就是说由绑定的关系,这样一来就是五个部分了。
- “发生->响应”的五个动作:
- 有一个事件
- 有一群人关注到这个事件
- 事情发生了
- 关心这个事件的人被通知
- 拿到信息的人根据事件参数对事件进行处理
小结
事件是用来对象或者类之间的信息传递与动作协调。
事件 = 事件的通知 + 可选的事件的参数(详细信息)
事件的应用
一个简单的小示例
using System;
using System.Timers;
namespace Hanoi
{
class Programme
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Timer timer = new Timer();//事件的发送者
timer.Interval = 1000;
Boy boy = new Boy();//事件的响应者
Gril gril = new Gril();
timer.Elapsed += gril.Action;
timer.Elapsed += boy.Action;//事件的订阅
timer.Start();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class Boy
{
internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e)//为了保持一致性,这里的定义是visual studio自动生成的
{
Console.WriteLine("Jump!!");//事件处理器
}
}
class Gril
{
internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Song!");
}
}
}
类型一:

using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Hanoi
{
class Programme
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Form form = new Form();
Recevier rev = new Recevier(form);
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class Recevier
{
private Form form;
public Recevier(Form from)
{
if(from != null)
{
this.form = from;
this.form.Click += this.FormClicked;
}
}
private void FormClicked(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.form.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
}
类型二:
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Hanoi
{
class Programme
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyForm form = new MyForm();
form.Click+=form.Action;
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class MyForm : Form
{
internal void Action(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
}
类型三:
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Hanoi
{
class Programme
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyForm form = new MyForm();
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
class MyForm:Form
{
private TextBox mytextbox;
private Button mybutton;
public MyForm()
{
mytextbox = new TextBox();
mybutton = new Button();
this.Controls.Add(mytextbox);
this.Controls.Add(mybutton);
mybutton.Height = 50;
mybutton.Left = 100;
mybutton.Top = 50;
mytextbox.Left = 100;
mybutton.Click+=this.Action;
}
private void Action(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.mytextbox.Text = "Hello,World";
}
}
}
制作自己的事件
事件声明的完整格式
可能会有一点点绕,但只要和委托事件结合起来,还是比较容易理解的。
using System;
using System.Globalization;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Threading;
namespace Hanoi
{
class Programme
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Customer customer = new Customer();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter();
customer.Order += waiter.Action;//事件连接
customer.Action();
}
}
public class OrderArgs
{
public string Size { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
public delegate void OrderHandller(Customer customer, OrderArgs e);
public class Customer
{
public int Bill { get; set; }
public void PaytheBill()
{
Console.WriteLine("I Will pay you {0} dollers", Bill);
}
public OrderHandller orderHandller;
public event OrderHandller Order
{
add { orderHandller = value; }
remove { orderHandller = value; }
}
public void Action()
{
Console.WriteLine("Walking Into the resturant");
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) { console.writeline("da da da"); thread.sleep(1000); } console.writeline("thinking ....."); for(int i="0;i<3;i++)" if(orderhandller !="null)//这里是指事件发生了,有没有人响应" this.orderhandller(this, new orderargs() name="Pizza" , size="large" }); class waiter internal void action(customer customer, orderargs e) switch(e.size) case "large": customer.bill +="10;" break; "small": default: console.writeline("you shoud pay{0} for the{1}",customer.bill, e.name); customer.paythebill(); < code>事件声明简化版本
public OrderHandller orderHandller;
public event OrderHandller Order
{
add { orderHandller = value; }
remove { orderHandller = value; }
}
if(orderHandller!= null)//这里是指事件发生了,有没有人响应
{
this.orderHandller(this, new OrderArgs() { Name = "Pizza", Size = "large" });
}
//将上述代码替换成
public OrderHandller orderHandller;
public event OrderHandller Order;
if(Order != null)//这里是指事件发生了,有没有人响应
{
this.Order(this, new OrderArgs() { Name = "Pizza", Size = "large" });
}
用 C#自带的事件处理器处理事件
using System;
using System.Globalization;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Threading;
namespace Hanoi
{
class Programme
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Customer customer = new Customer();
Waiter waiter = new Waiter();
customer.Order += waiter.Action;//事件连接
customer.Action();
}
}
public class OrderArgs:EventArgs
{
public string Size { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
public class Customer
{
public int Bill { get; set; }
public void PaytheBill()
{
Console.WriteLine("I Will pay you {0} dollers", Bill);
}
public event EventHandler Order;
public void Action()
{
Console.WriteLine("Walking Into the resturant");
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) { console.writeline("da da da"); thread.sleep(1000); } console.writeline("thinking ....."); for(int i="0;i<3;i++)" if(order !="null)//这里是指事件发生了,有没有人响应" this.order(this, new orderargs() name="Pizza" , size="large" }); class waiter internal void action(object customer, eventargs e) customer cus="customer" as customer; orderargs args="e" orderargs; switch(args.size) case "large": cus.bill +="10;" break; "small": default: console.writeline("you shoud pay{0} for the{1}",cus.bill, args.name); cus.paythebill(); < code>事件的书写规范
protected void OnOrder(object customer,OrderArgs args)
{
if (Order != null)//这里是指事件发生了,有没有人响应
{
this.Order(customer, new OrderArgs() { Name = "Pizza", Size = "large" });
}
}
//事件的专属触发器用On+动词命名
小结
通过上述例子也可以得知,事件就是委托类型的包装器,包装器对委托的字段起到了限制的作用,也就是委托的参数只能由事件发起者自己来传递,而不由别人传递
